
Small business KPIs, short for key performance indicators, allow you to evaluate a specific area of your company’s health. There are countless KPIs a business can potentially track. While you don’t need to monitor them all, it’s good practice to monitor a few that can help you gauge your company’s overall health and track select KPIs that correlate with your strategic objectives and align with specific goals. We’ll walk you through some of the most common on this page.
1. Revenue Growth Rate
Revenue growth rate is a helpful metric to track, especially for startups. It’s a measure of how much your company grew over a period of time. Most businesses use monthly revenue figures in their calculations, though high-growth firms in the early stages may measure weekly.
How to Measure Your Revenue Growth Rate
Growth Rate = (Current Period’s Revenue – Previous Period’s Revenue) / Previous Period’s Revenue
2. Gross Profit Margin
Gross profit margin is a basic way to gauge your company’s financial health. It’s the profit that remains after you subtract the cost of goods sold (COGS) from your revenue. Whereas gross profit is represented as a dollar amount, gross profit margin is shown as a percentage. If your gross profit margin is high, it indicates that your business’s profit exceeds its costs.
How to Measure Your Gross Profit Margin
Gross Profit Margin = (Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold) / Revenue x 100
3. Net Profit Margin
Net profit margin is similar to gross profit margin, but it provides a clearer picture of profitability because it uses net income, also called net earnings or net profit. This is your total sales minus all costs, including COGS, operating costs, general expenses, taxes, and interest. Because of this, it’s the small business KPI that analysts and investors are more likely to scrutinize.
How to Measure Your Net Profit Margin
Net Profit Margin = (Net Income / Revenue) x 100
4. Customer Acquisition Cost
Customer acquisition cost (CAC) is one of your most important marketing KPIs. As the name suggests, it’s the total cost your business pays to lock in a single customer over a specific period.
Cost of customer acquisition includes all sales and marketing expenses during the period, including salaries, bonuses, commissions, overhead, and marketing spend from the lead generation stage through the close of a sale.
CAC declines as you refine your marketing strategy, and ROI increases. Generally speaking, it’s best to have the lowest CAC possible. However, there are times when an unusually low CAC could signify trouble. For instance, your CAC may be low if your sales team is rushing through the process or using aggressive tactics. Unfortunately, these customers will likely leave your company quickly, so it’s better to invest more in your CAC.
How to Measure Your Customer Acquisition Cost
Customer Acquisition Cost = Cost of Sales and Marketing / Number of New Customers Acquired
5. Customer Lifetime Value
Customer lifetime value, sometimes shortened to CLV or CLTV, measures the revenue you can expect to generate from a customer the entire time they’re with your company.
CLV can help you determine how much to invest in customer acquisition and identify reasonable budgets for your marketing campaigns. It can also help you identify how much to invest in customer retention.
How to Measure Your Customer Lifetime Value
Customer Lifetime Value = (Average Customer Purchases Per Cycle x Average Customer Life Cycles)
6. Sales Conversion Rate
A sales conversion rate is used to measure the effectiveness of a sales team or sales strategy. A high conversion rate indicates that a large portion of potential customers are becoming actual customers. You’ll usually want your conversion rate as high as possible.
How to Measure Your Sales Conversion Rate
Sales Conversion Rate = Total Number of Sales / Total Number of Qualified Leads x 100
7. Customer Satisfaction Score
Happy customers are more likely to stay with your company, make larger purchases, purchase more often, and refer their friends. It’s crucial to proactively measure customer satisfaction and make changes as needed to improve your overall odds of long-term success.
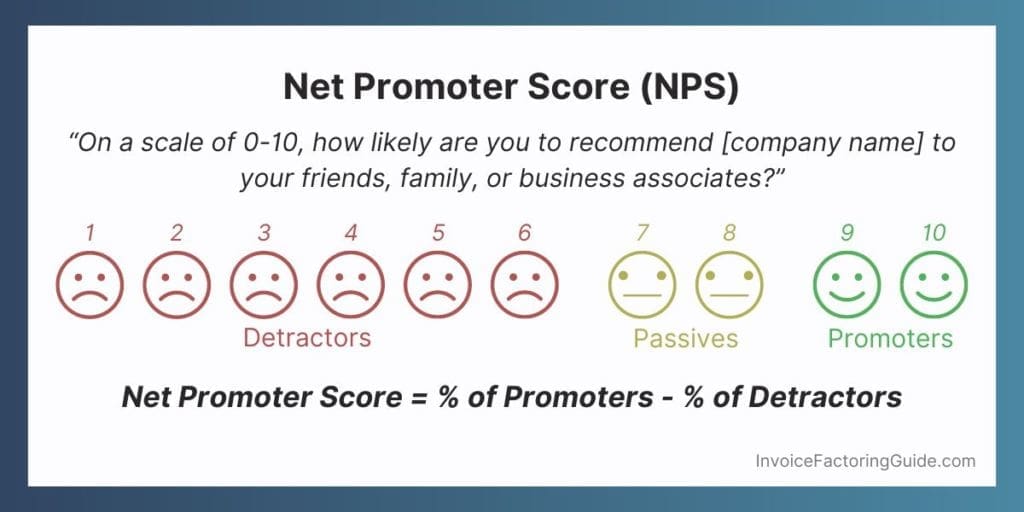
The most common and often most straightforward way to measure customer satisfaction is with a net promoter score. It involves asking your customers a single question: “On a scale of 0-10, how likely are you to recommend [company name] to your friends, family, or business associates?”
Those with a rating of nine or ten are your biggest fans, referred to as “promoters.” They’re typically loyal to you and either are already long-term customers or will be. They’re probably referring people to you already, too.
Anyone who provides a rating of seven or eight is considered passive. Their opinion may sway depending on their most recent experience with your brand.
Those who provide a rating of six or lower are your detractors. They’re not happy and aren’t likely to stay with your business long.
How to Calculate Your Net Promoter Score
Net Promoter Score = % of Promoters – % of Detractors
8. Cash Flow Forecast
Eight in ten small business failures can be traced back to poor cash flow management, the National Federation of Independent Business (NFIB) reports. This is because even small shifts in cash flow can make it impossible for a small business to keep up with important expenses, such as payroll and supply orders. A cash flow forecast, also called a cash flow projection, is one of the most critical small business KPIs to track because it can help you identify potential cash flow shortfalls before they happen.
Pay attention to the margin, even if it’s positive. A significant variance could indicate that you’re not putting your cash to work for your business. You might want to invest in growth initiatives. Meanwhile, a narrow margin signifies your business could still run short. You’ll want to take corrective action or set up a backup funding source in these cases.
How to Forecast Cash Flow
Cash Flow Forecast = Estimated Income – Estimated Expenditures
Strengthen Your Small Business KPIs with Factoring
Whether your cash flow forecast indicates you might have a shortfall or you need working capital to invest in initiatives to improve your other small business KPIs, invoice factoring can help. Rather than taking out a loan or leveraging a line of credit, factoring unlocks the cash you’ve already earned that’s trapped in your unpaid B2B invoices. Check out our Invoice Factoring Guide for more information on how the process works, or request a complimentary rate quote to get started.


About Invoice Factoring Guide
Related Articles
Get an instant funding estimate
Results are estimates based on the calculated rate and the total invoice amount provided.
Actual rates may vary.
Request a Factoring Rate Quote
PREFER TO TALK? Call us at 1-844-887-0300










